Sensing and errors
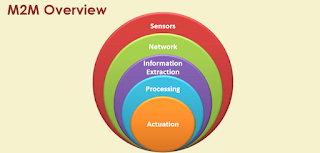
The internet of things is based on two main concepts that are sensing and actuation. The sensing and actuation are totally mutually dependent. If sensing is the reason then actuation helps to produce the result.
Vector sensor-
The definition of sensing may be stated as a sensor detects or senses the condition of its peripheral condition in other words "A device which detects or measures a physical property and records, indicates or otherwise respond to it -Oxford dictionary".
All the sensors take some input from the environment or sense some physical changes. The senses act as a stimulus to a sensor for example heat is converted into electrical signal or pressure is converted into electrical signal. All the stimulus are converted into electrical signal. For converting the physical signals into the electrical signal there is a component that is called transducers. The transducer converts the energy of one kind into another energy.
Sensors vs Transducer :
The sensor is the one component but Transducer is the collection of sensors as well as actuators. Sensors are used to sense a wide range of different energy and Actuators are used to switch voltages and current.
Sensor resolution:
- The resolution of a sensor is the smallest change it can detect the quantity that is measuring.
- Digital resolution of a sensor with a digital output is the smallest resolution of the sensor.
- The more resolution of a sensor, the more accurate is its precision of the sensor.
- A sensor's accuracy doesn't depend upon its resolution.
examples of sensors-
pressure sensor-
source-https://www.sensorsmag.com/components/pressure-sensor-roundup-part-two
Ultrasonic Distance Sensor-
source-https://www.google.co.in/search
Camera Sensor-
source-https://www.google.co.in/search
Sensor Classes:
There are two classes of the sensor and they have two categories.
Based on o/p- Analog and Digital
Bases on Data Type-Scalar and vector
Analogue sensors:
- Analogue sensors produce a continuous or a linear signal o/p or voltage which is generally proportional to the quantity being measured.
- Physical properties like speed, temperature, displacement are the example of analogue quantities. The temperature of the water is measured using a thermocouple or a thermometer which continuously respond to temperature changes of the water.
Digital sensor-
- Digital signal produces discrete o/p signals or voltages that are a digital representation of the quantity being measured.
- Digital sensors are produced by binary o/p signal in the form of "1" or "0".
- Digital signals produce only discrete values which may be output as a single "bit" that is called "serial transmission" or by combining bits to produce "bytes" that is called "parallel transmission".
source-https://www.google.co.in/search
Scalar Sensor-
- The scalar sensor produces the o/p signal which is generally proportional to the magnitude of the quantity being measured.
- Physical properties like temperature, pressure etc. all are scalar quantities. Only their magnitude is sufficient to convey the information.
- For example, the temperature of a room can be measured by the thermometer or by a thermocouple which response to the changes of the temperature irrespective of the orientation of the device.
- Vector sensor produces the o/p signal which is generally proportional to the magnitude of the quantity being measured and as well as the orientation of the quantity being measured.
- Physical quantities like sound, acceleration etc. all are vector sensor.
- For example, the acceleration of a body can be measured by an accelerometer which gives the components of acceleration of the body with respect to x,y,z coordination.
Deviation of Sensors:
- The range of the o/p of a sensor is always limited. There are a minimum and maximum value of a sensor.
- The sensitivity of a sensor may differ from the value that is specified.
- The o/p signal differs from the specified value that is called sensitivity error.
- The o/p signal differs from the correct value by a constant that is called offset error or bias.
Non-linearity:
- Non-linearity is the deviation of the sensor.
- This is defined as the amount of o/p differs from the ideal transfer function behaviour from the full range of the sensor.
- Most sensors have the linear behaviour.
If the o/p signal slowly changes independent of the measured property that is called drift.
Noise is the random deviation of the signal that varies in time.
Hysteresis Error:
Noise is the random deviation of the signal that varies in time.
Hysteresis Error:
- If the present o/p of a sensor is depending on the previous input and some error occurs that is called hysteresis error.
- Analogue sensors, the magnetic sensor shows this type of error.
other errors are quantisation error, aliasing errors etc.
- If the sensor has a digital output, the o/p is essentially an approximation of the measured property. The error is called quantisation error.
- If the signal is monitored digitally, the sampling frequency can cause a dynamic error or if the i/p variable or added noise changes periodically at a frequency proportional to the multiple of the sampling rate then the aliasing errors may occur.
The sensors may be sensitive to the properties other than the property being measured for example most of the sensors are sensitive to the temperature of the environment.
to be continued........







Thanks for sharing this valuable information regarding
ReplyDeletewill help you more:
ValveFittingStore.com an exclusive online distributor for ANIX Pneumatic Actuator, ANIX Y-Strainer, ANIX Sanitary Valve and All-Torque Electrical Actuators.
http://www.valvefittingstore.com